Introduction
Bees play an incredibly crucial role in agriculture and the wider ecosystem. These tiny creatures are often seen as mere nuisances when they buzz around, but their contribution to food production and biodiversity outweighs any discomfort they might cause. Let’s dive deeper into why bees are essential and explore the urgent need for innovative solutions to support them.
Importance of Bees in Agriculture
Imagine biting into a juicy apple or savoring the sweetness of a ripe strawberry. Behind these delicious fruits lies a story of intricate relationships, primarily involving our buzzing friends, the bees. Approximately 75% of global food crops rely on pollinators, with bees being the most effective among them. Their vital role includes:
- Pollination: Bees transfer pollen from the male parts of a flower to the female parts, allowing plants to produce fruits, seeds, and vegetables. This natural process not only promotes plant health but also boosts crop yields.
- Biodiversity Support: By pollinating a wide variety of plants, bees help maintain biodiversity, which is essential for resilient ecosystems. More biodiversity means more reliable food sources for future generations.
- Economic Contribution: In the United States alone, bees contribute an estimated $15 billion to the agricultural economy through increased crop production. This figure skyrockets globally, underlining their immense value.
Growing up, I remember visiting my grandparents’ farm where bees buzzed around the wildflowers and fruit trees. The sheer abundance of produce was a wonder to me, and it’s evident that without bees, many of these fruits and vegetables would simply vanish from our tables. You might find it surprising to know that strawberries, for example, yield 30% more fruit when pollinated by bees! However, despite their vital contributions, bee populations are in decline due to various factors. This brings us to a significant concern: the pressing need for innovative solutions that can safeguard not only bees but also the future of agriculture.
Need for Innovative Solutions
With the alarming decline in bee populations attributed to habitat loss, pesticide usage, climate change, and diseases, farmers and researchers are on a quest for sustainable strategies that protect the honeybee and other pollinators. It’s not just about conserving a species; it’s about preserving our food supply. Here are several reasons why innovative solutions are paramount:
- Farmers’ Reliance: Many farmers depend heavily on honeybee rentals for their crops. With bee populations dwindling, farmers face increased challenges in securing sufficient pollination services.
- Alternative Pollination Methods: Traditional methods of beekeeping are being complemented by innovative technologies like bee drones. These technological advances promise to fill the gaps left by declining bee populations and ensure that crops continue to thrive.
- Sustainable Practices: Farmers are increasingly aware of the need for environmentally friendly practices. Innovative solutions can help balance agricultural productivity with ecological conservation.
To illustrate, take the case of commercial apple orchards that heavily rely on pollination. If the honeybee population continues to decline, the apple harvest could suffer tremendously. Farmers may have to resort to expensive and less effective alternatives, pushing the price of apples up. This ripple effect affects not just farmers but consumers too – everyone feels it at the grocery store. A prime example of an innovative solution is the development of artificial pollinators that mimic the natural behavior of bees. These technologies can be integrated into smart farming practices, which can greatly enhance crop production while minimizing reliance on natural bee populations. As you can see, the importance of bees in agriculture is profound. Not only do they impact the quantity of food produced, but they also influence the variety and safety of our food supply. The need for innovative solutions has created a new frontier in agriculture, merging technology with nature to protect our essential pollinators. In the following sections, we’ll explore the emergence of bee drones as a viable alternative to traditional beekeeping, highlighting their advantages, current applications, and the technology behind them. This exploration will showcase the intersection of innovation and agriculture, setting us on the path toward a sustainable future. Stick around, as it’s an enlightening journey devoid of buzzwords, but filled with the wonders of nature and technology working hand-in-hand!
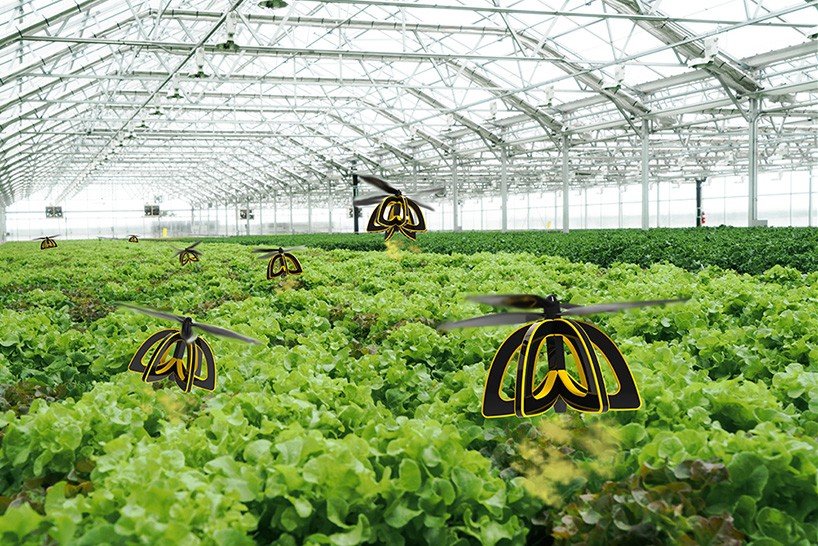
The Rise of Bee Drones
As we venture into the realm of innovative solutions to support agriculture and pollination, the rise of bee drones is nothing short of fascinating. These technological marvels are quickly changing the landscape of pest control and crop pollination. They offer a host of advantages over traditional beekeeping, which harks back to centuries of farming practices.
Advantages Over Traditional Beekeeping
While traditional beekeeping has its roots deep in history, modern challenges require modern solutions. Bee drones provide several advantages that address the shortcomings we face today. Let’s break down how they stack up against traditional methods:
- Predictable Pollination: Unlike honeybees that can be unpredictable in their activities, bee drones can be programmed to operate during optimal times for pollination, ensuring more consistent results. Imagine a farmer knowing exactly when their fields will be pollinated rather than depending on the vulnerable weather and habitat conditions—this predictability offers a sense of security.
- Reduced Labor: Managing a beehive requires considerable skill and time. Bee drones can significantly reduce the labor associated with pollination, freeing farmers to focus on other aspects of their operations. For instance, if you’ve ever watched a beekeeper suit up and inspect hives, you can appreciate how labor-intensive this work is. With drones, that time can be saved.
- Minimizing Environmental Impact: Traditional beekeeping often involves transporting hives across large distances for pollination purposes, which can disturb ecosystems and increase the risk of diseases. Bee drones can be deployed directly to fields without displacing any hives.
- Precision Pollination: Drone technology allows for targeted pollination, focusing on specific plants, which can minimize the competition among plant species for resources. This precision can lead to increased efficiency, as drones can access hard-to-reach flowers and locations where bees may not thrive.
- Reduced Risk of Colony Collapse Disorder: With the alarming rates of colony collapse disorder affecting honeybee populations, relying on bee drones offers a fail-safe method for crop pollination without the associated risks of bee health issues.
With these advantages in mind, it’s clear that bee drones can enhance agricultural practices while taking the pressure off natural bee populations. As I think back to my childhood, I recall the times when my family used to rely heavily on bees for our garden flowers and fruits. If only we’d had this technology back then!
Current Applications in Agriculture
The utility of bee drones isn’t just in theory. Innovative agricultural practices are already embracing this new technology, showing real-world applications that are changing how crops are pollinated. Here’s a closer look at how bee drones are currently being utilized in the field:
- Fruit Orchards: Many farmers are deploying bee drones in fruit orchards to ensure timely pollination. For instance, cherry and apple orchards benefit greatly from consistent drone activity, particularly during the critical blooming period. The outcomes have been promising, with reports indicating increased fruit set and quality.
- Nut Trees: Just as with fruit, nut trees such as almonds are incredibly sensitive to pollination timing. Farmers have started to supplement honeybee activity with drones to improve pollination during essential blooming times. This has helped mitigate some of the challenges associated with the declining bee population.
- Greenhouses: In controlled environments like greenhouses, using bee drones makes perfect sense. They can be deployed to efficiently pollinate flowering crops without the spatial limitations and risks associated with live bees. This setting allows for precise and controlled applications, elevating the potential yield quality.
- Specialty Crops: Crops like blueberries and cranberries, which are particularly challenging to pollinate naturally, have seen promising results with the introduction of bee drones. Farmers have reported effective coverage and significantly higher yields when drones are employed alongside or in place of traditional pollination methods.
- Research and Development: Ongoing studies explore enhancing drone technology to mimic the buzzing frequency and movement patterns of living bees. This could further improve pollination effectiveness, making drones even more appealing for future agricultural practices.
As we witness the rise of bee drones, it becomes evident that technology is not only supporting our agricultural needs but also fostering a sustainable approach to pollination. With the ability to integrate these drones into existing frameworks, farmers can adopt a hybrid strategy that combines the best of bees and technological enhancements. Looking forward, you’ll notice that as we navigate through potential challenges and limitations associated with this technology, the promise it holds will pave the way for a groundbreaking shift in agriculture. Join me as we explore the fascinating world of bee drone technology and its impact on crop pollination!
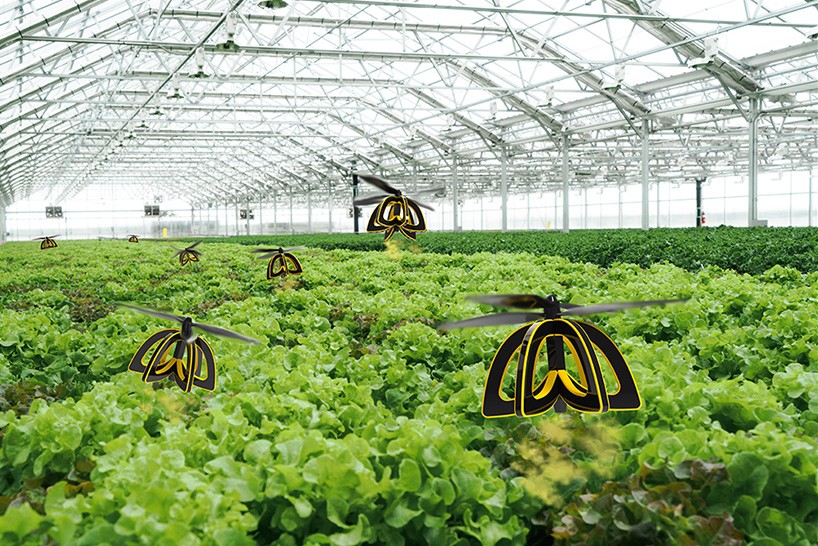

Bee Drone Technology
As we dig deeper into the world of bee drones, it’s essential to appreciate the clever design and sophisticated technology that make these devices effective pollination allies. The combination of innovative components and cutting-edge navigation systems is what sets bee drones apart in today’s agricultural landscape. Let’s break it down.
Design and Components
Bee drones are not just any ordinary flying gadgets; they’re specifically crafted to replicate the natural behavior of pollinators while maximizing efficiency. Their design includes several key components that work harmoniously to achieve this objective:
- Lightweight Frame: The structure of bee drones is engineered to be lightweight yet durable. Made with advanced materials such as carbon fiber or specialized plastics, these drones can quizzically hover without the cumbersome weight, allowing for better maneuverability.
- Pollination Mechanism: Instead of traditional rotors, many bee drones utilize a unique pollination mechanism that mimics the gentle landing and take-off behavior of bees. Some models feature vibrating pollen dispensers that distribute pollen effectively as the drone hovers, ensuring better flower coverage. Picture a drone gently gliding to a flower, delivering pollen just as a bee would—it’s remarkable!
- Power Source: The power systems in bee drones are designed for extended operation times. Lithium-polymer batteries provide the necessary energy while remaining lightweight. In some advanced models, solar panels are integrated, allowing drones to recharge during the day, making them sustainable workers in the field.
- Sensors and Cameras: Equipped with a range of sensors and cameras, bee drones can assess floral health and environmental conditions. These components help them detect which plants need pollination, analyze flower characteristics, and avoid obstacles. Imagine being able to “see” whether a flower is ripe for pollination—that’s precisely what these drones can do!
- Pollen Collection Chambers: Some drones are fitted with specialized chambers that collect pollen from pollinator crops or storage sites. This ensures that the drones carry sufficient pollen to perform effective pollination as they zip from flower to flower. It’s like having a tiny cargo hold onboard!
I vividly remember the time my father tried to pollinate our backyard garden by hand, only to watch my efforts go to waste as I missed some blooms. If only we had had a bee drone then! Watching this technology flourish today shows the substantial innovations occurring in agriculture.
Navigation and Control Systems
Navigating the complexities of agricultural environments requires sophisticated and precise control systems. Bee drones are equipped with advanced technology that enables them to effectively and efficiently cover large areas while ensuring successful pollination. Here’s how:
- GPS Technology: Most bee drones incorporate GPS technology, allowing them to pinpoint locations with remarkable accuracy. This enables farmers to set specific coordinates for pollination routes, ensuring that no valuable plants are overlooked. GPS also allows drones to return to their starting point after completing their tasks, much like trained bees returning to their hive.
- Autonomous Flight Capabilities: Bee drones can operate autonomously thanks to advanced algorithms that monitor conditions and determine optimal flight paths. They can adapt to various agricultural layouts and circumstances, adjusting their routes and behavior accordingly. If you’ve ever flown a drone, you know how exhilarating yet challenging it can be; imagine a drone that autonomously navigates through complex fields!
- Obstacle Detection and Avoidance: Equipped with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors and cameras, bee drones can detect and avoid obstacles in real-time. This feature helps them maneuver around crops, trees, and other unexpected impediments seamlessly, reducing the risk of accidents. This technology mimics the keen senses of real bees, making the journey through the field safe and efficient.
- Remote Control and Monitoring: Farmers can monitor bee drone operations and manage tasks through user-friendly interfaces or mobile applications. This means they can check in on operations in real time, adjust settings, and even receive status updates about pollination results. It’s all about staying informed and connected!
- Data Integration: One of the more exciting aspects of bee drone technology lies in its ability to collect data. Drones can gather information about pollination success rates, environmental conditions, and plant health, feeding this data back to farmers. This wealth of information is invaluable for making informed decisions about crop management.
As you can see, bee drones represent a confluence of design ingenuity and smart technology, making them truly remarkable tools for modern agriculture. Looking forward, the capabilities of bee drones will continue to evolve alongside advancements in technology. As we explore the impact of this technology on crop pollination, it’s important to recognize both the promises and potential challenges ahead. So let’s journey forward to uncover how these innovations are reshaping farming practices for a sustainable future!

Impact on Crop Pollination
With bee drones making waves in agriculture, it’s crucial to examine their tangible impact on crop pollination. Their introduction brings a new layer of efficiency and effectiveness to the table, and understanding this transformation sheds light on how modern farming practices evolve. Let’s explore how bee drones enhance crop pollination and compare it to naturally occurring bee pollination.
Efficiency and Effectiveness
When it comes to pollination, the efficiency and effectiveness of bee drones are impressive, and they’re reshaping the standards by which we gauge success in agriculture. Here are several factors showcasing how drones excel:
- Speed of Deployment: Bee drones can quickly be deployed across vast areas, significantly reducing the time required for pollination—especially when compared to the movements of natural bee colonies. For instance, if you’ve ever watched a field of flowers being pollinated by hand or with traditional hives, you’ll appreciate how much faster drones can complete this task.
- Targeted Pollination: Drones can be programmed to focus on specific crops and locations. This means that every plant can receive the required attention without having to rely on the natural foraging habits of bees, which may overlook certain areas, especially in large farms. For example, in an almond orchard, farmers have found that drone-assisted pollination can cover all trees, ensuring higher yield rates.
- Constant Operation: Unlike bees, which are affected by weather conditions and the time of day, bee drones can operate under various conditions. While rain and wind might deter natural bees, drones can be designed to withstand different environmental variables, ensuring that pollination happens as scheduled. Imagine being able to pollinate even when it’s overcast!
- Quantifiable Results: One significant advantage of using drones is the ability to gather data and assess their effectiveness. Farmers can track which flowers were pollinated, monitor pollen distribution patterns, and measure the resulting yield. This data-driven approach allows for constant refinement of practices. With traditional beekeeping, such metrics aren’t readily available, making it harder to gauge efficiency.
In a practical example, farmers at a large agricultural convention demonstrated improved yields of nearly 30% when utilizing bee drones for a trial run on crops like blueberries. Such statistics are convincing and highlight the potential of these technological marvels in maximizing agricultural productivity.
Comparison with Natural Bee Pollination
As we delve into the comparison between bee drones and natural bee pollination, it’s important to recognize the strengths and weaknesses of each. Both systems have their unique benefits, and understanding these can help farmers make more informed decisions.
- Diversity vs. Precision: Natural bees contribute to biodiversity by pollinating a wide range of plant species. This diverse pollination supports other wildlife, while bee drones focus on maximizing the yield from specific crops. Think of this as a trade-off—natural bees nurture ecosystems, while drones hone in on farming productivity.
- Bees’ Foraging Behavior vs. Drone Programming: Natural bees exhibit complex foraging behaviors driven by instincts and environmental cues. This often results in unpredictable and sporadic pollination patterns. In contrast, bee drones operate based on pre-programmed routes and tasks, resulting in a consistent and reliable pollination schedule.
- Nutritional Quality of Crops: Studies suggest that crops pollinated by natural bees might have a higher quality in terms of flavor and nutritional value. This stems from the bees’ natural behaviors and preferences for healthy, diverse food sources. Drone-pollinated crops can achieve size and quantity; however, farmers might need to consider potential differences in quality and taste.
- Costs and Sustainability: While investing in bee drones can be costly upfront, operational expenses may decrease over time due to their efficiency and reduced reliance on live bee colonies. Additionally, in areas where bee populations are struggling, drones can provide a sustainable backup for pollination needs without disrupting natural ecosystems.
While there is no debate about the invaluable role bees play in supporting nature and agriculture, the surge of technology like bee drones opens up new avenues for sustainability. As we embrace these advancements, it’s vital to strike a balance between technological solutions and the well-being of natural bee populations. This synergy can ensure that we foster thriving ecosystems while optimally feeding the growing global population. The journey doesn’t stop here. Join me as we explore the potential challenges and limitations of bee drones in agricultural practices, paving the way for more informed decisions as we push forward into a sustainable agricultural future!
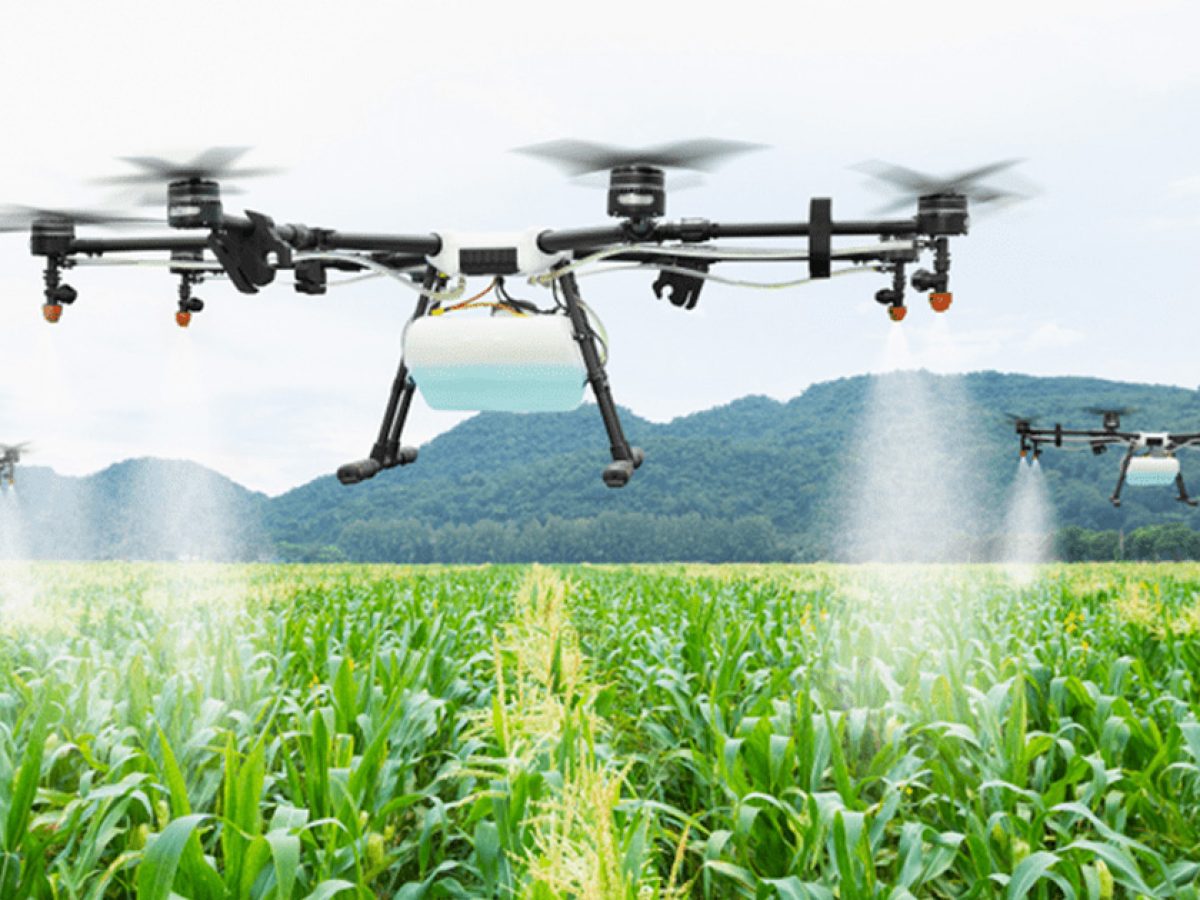

Potential Challenges and Limitations
As promising as bee drones can be in revolutionizing agricultural pollination, they are not without their challenges and limitations. Understanding these aspects is crucial for farmers and stakeholders to adapt wisely as they incorporate this technology into their practices. In this section, we will delve into the environmental concerns and regulatory hurdles associated with bee drones.
Environmental Concerns
When introducing any new technology into agriculture, it’s vital to consider potential environmental impacts. Bee drones, while innovative, raise several concerns that warrant attention:
- Impact on Bee Populations: While bee drones are designed to supplement pollination, there is a fear that they could inadvertently undermine natural bee populations. For instance, if farmers prioritize drone use over maintaining healthy bee hives, this could exacerbate the decline of natural bee populations that are crucial for biodiversity. Imagine a scenario where farmers rely solely on drones, leading to fewer flowers being visited by real bees, disrupting the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
- Energy Consumption and Emissions: The energy used to operate drones must come from somewhere. Depending on the power source, drone usage could contribute to carbon emissions. While many drones utilize rechargeable batteries, the environmental footprint of producing and disposing of these batteries is an important consideration. How will this square with the goal of sustainable agriculture? It’s a question that innovators and farmers must continue to ponder.
- Pollution from Pollen Dispersal: If not meticulously managed, drone-pollinated crops could introduce excessive artificial pollen into the environment. This could potentially create imbalances within ecosystems, leading to cross-pollination with native flora that may not be adapted to those pollen sources. As we move forward, we must ensure that drone technology works in harmony with nature rather than disrupt it.
- Wildlife Interactions: The presence of drones in agricultural spaces could have unintended consequences on local wildlife. Birds or other animals might be disturbed by drone operations, leading to changes in their behavior or habitat use. This disruption can elevate stress levels in wildlife, adversely affecting entire ecosystems.
As someone who always marveled at the connection between nature and technology, I can’t help but think back to a garden I once tended. It thrived because of the balance of its ecosystem. Any technology that disrupts this balance warrants careful examination. After all, maintaining that harmony is key to sustainable farming.
Regulatory Hurdles
Moving forward with bee drones also involves navigating a complex maze of regulatory challenges. These hurdles can slow down adoption and innovation, so it’s important to address them head-on:
- Lack of Standardization: The technology around bee drones is still relatively new, which means a lack of established standards and guidelines. Without standardization for drone design, usage, and safety protocols, farmers might be hesitant to adopt this technology, fearing liability or ineffective implementation. Just as we need guidelines for good beekeeping practices, drone operators require a framework to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Legal Restrictions on Drone Use: Many countries have strict regulations concerning drone usage, particularly in agricultural settings. These regulations can vary widely, with some regions requiring special permits or additional licenses. For example, farmers in densely populated areas or regions with wildlife conservation laws may find additional barriers to using drones. Navigating these regulations could become a significant hurdle for prospective users.
- Liability and Insurance Issues: As with any new technology, property damage or accidents involving drones could raise concerns about liability. Ensuring that those operating drones are protected under existing agricultural insurance policies could prove challenging. Farmers need assurance that they won’t face substantial financial risks just for trying out a new pollination method.
- Public Perception Concerns: There’s often skepticism surrounding new technologies, especially in agriculture. Many people may view drone usage with suspicion, fearing negative environmental impacts or unintended consequences. Educating the public and fostering trust in this technology is going to be crucial for its acceptance.
Navigating the regulatory landscape while addressing environmental concerns will require collaboration among stakeholders. Farmers, regulators, and technology developers must work harmoniously to create a framework that ensures that bee drones can be utilized safely and effectively. In conclusion, while bee drones hold remarkable potential to augment agricultural practices, it’s essential to consider the challenges and limitations that come with them. As we strive for a balance between innovation and environmental stewardship, the path forward will involve dialogue, regulation, and careful monitoring. The next essential step is to cultivate ongoing research and development that can address these challenges head-on, leading to solutions that respect both our ecosystems and the farmers who rely on them. Let’s continue this journey into the future of agriculture, uncovering promising developments and breakthroughs on the horizon!
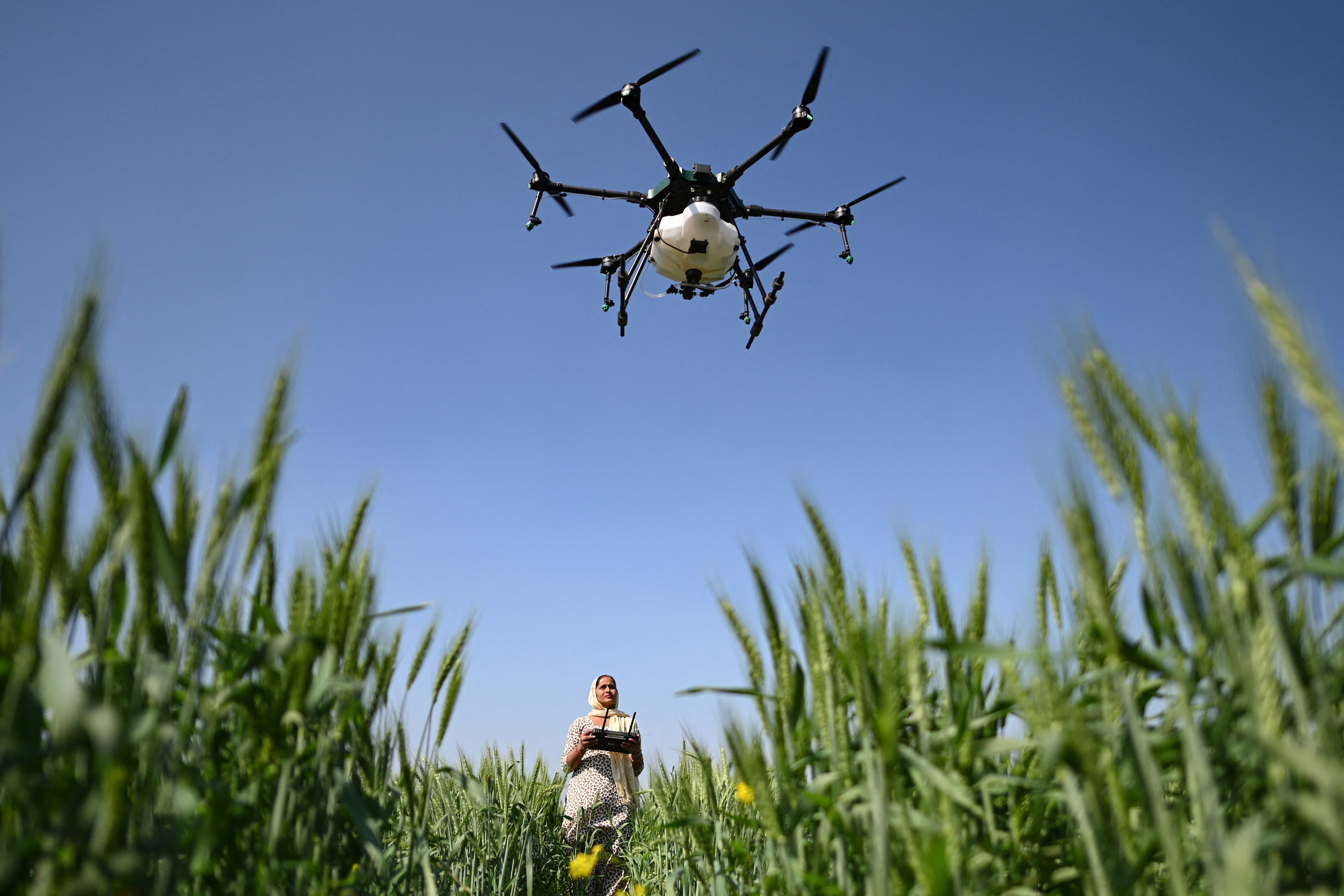

Future Developments and Research
As we look toward the horizon of agricultural technology, the potential for future developments and research surrounding bee drones is truly exhilarating. With ongoing advancements in drone technology and a shift toward smarter farming practices, the landscape of agriculture could change dramatically in the coming years. Let’s explore what these enhancements entail and how they work together to create a sophisticated farming ecosystem.
Enhancements in Drone Technology
The future of bee drones is promising, with numerous technologies on the cusp of revolutionizing how we think about pollination. Here are a few key areas where enhancements may take place:
- Improved Autonomy: Current drones rely on basic programming and GPS technology to navigate and pollinate crops. Future advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) could lead to fully autonomous drones that can adapt to changing environmental conditions in real-time. Imagine drones intelligently adjusting their routes based on wind patterns or flower growth phases—this adaptability could significantly enhance pollination rates.
- Advanced Sensors: Researchers are continually working on integrating cutting-edge sensors that can better assess plant health, climate conditions, and soil moisture levels. A drone equipped with multi-spectral imaging sensors could identify which plants are in desperate need of pollination and prioritize them. This level of insight would allow farmers to maximize their resources and deliver precisely the support plants require.
- Swarm Technology: Just like bees, which often operate in unison, future bee drone technology could leverage swarm robotics. Small drones could work collaboratively, communicating with each other to efficiently cover vast agricultural fields. This capability would allow for a collective approach to pollination, increasing coverage and efficiency. Think of a coordinated dance of drones, each playing its role to amplify pollination!
- Battery Innovations: As battery technology improves—especially with developments in lightweight battery materials and increased energy density—future drones may operate longer and with shorter charging times. This means more extended flights, minimizing downtime, and maximizing pollination coverage over the course of a farming season.
Seeing these innovations in action reminds me of a local farmer’s market I often visit, where the variety and quality of produce reflect years of hard work and adaptation. Imagine all of that rich, vibrant produce being supported by even more technologically enhanced pollinating efforts!
Integration with Smart Farming Practices
Bee drones are only part of the equation. The integration of these advanced drones with smart farming practices can transform agricultural sustainability. Here’s how this synergy may unfold:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: As bees drones collect data on pollination efficiency, they can feed this information into a centralized farm management system. Smart farming practices rely heavily on data analytics, which can help farmers understand trends, optimize planting schedules, and make better resource allocation decisions. This means fewer chemicals need to be used, reducing the environmental impact.
- Soil and Crop Management Systems: Future smart farms will have integrated systems that monitor not just pollination but also other vital areas such as soil health and crop conditions. Bee drones working in tandem with soil sensors and moisture detectors can create a comprehensive ecosystem that informs farmers about all aspects of farm management.
- Precision Agriculture: Combining bee drones with precision agriculture techniques can lead to a new era of efficiency. For instance, a farmer may use satellite imagery alongside drone data to assess not only which areas need pollination but also how much water and fertilizer each section requires. This approach could significantly reduce waste and enhance productivity, making farming more sustainable.
- Autonomous Farming Equipment: Dramatic changes will occur in the agricultural logistics landscape as drone technology integrates with other autonomous solutions. Farmers may find themselves utilizing self-operating machinery that works alongside bee drones to deliver resources and maintain crops without constant human oversight.
- Platform for Collaborative Research: Just as we see communities come together to enhance agricultural practices, future integrations may involve partnerships among farmers, technologists, and researchers. With platforms that share drone data among users, everyone can learn from one another, encouraging continuous advancement through collaborative research efforts.
This interconnected approach resonates with me, as I recall visiting a pioneering farm that implemented smart technology to optimize operations. The way they adjusted practices based on data provided insights I never knew could shape the future of farming! In summary, as we gaze into the future of bee drones, it’s clear that the journey will not only be shaped by technological advancements but also by how these innovations are integrated into the broader framework of smart farming. This evolution promises an exciting future for agriculture where sustainability, efficiency, and productivity can flourish hand in hand. So, as we move forward, let’s keep our eyes peeled for developments on both the technological front and the sustainable farming frontier. The world of agriculture is expansive, and it’s poised for groundbreaking changes that can better connect us to the food we grow and eat. Here’s to the future—a future that champions both technology and the natural world!


