Introduction to Drones
When you think about drones, you might envision sleek machines buzzing overhead, capturing stunning aerial photographs and delivering packages at record speeds. Drones have indeed come a long way from their early beginnings, transforming into indispensable tools across various sectors. Let’s take a closer look at the fascinating history of drones, as well as the various types available today.
History of Drones
The concept of using flying machines without a pilot traces back to the early 20th century. Although the term “drone” is a modern coined word, the roots of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be found in military innovation.
- World War I: One of the earliest uses of drones occurred during WWI, with military experiments involving remote-controlled aircraft. The U.S. military developed “Kettering Bug,” a drone designed to carry explosives over enemy lines. However, it was never used in combat.
- Interwar Period & World War II: During the interwar years, drones began to take shape through experiments. By World War II, UAVs, including the “Radioplane OQ-2,” which was developed by actor and inventor Howard Hughes, were being used for target practice and reconnaissance.
- Cold War Era: As military needs evolved, so too did drone technology. The Cold War spurred advancements in reconnaissance drones, most notably the A-12 Oxcart and the later drones used during conflicts in Vietnam.
- Modern Era: The significance of drones extended beyond military purposes. In the early 2000s, the rise of hobbyist drones democratized drone technology, allowing the general public to access UAVs for fun and practical uses. Companies like DJI revolutionized the consumer market, producing drones equipped with high-definition cameras and user-friendly controls.
Today, drones are prolific, entering arenas such as agriculture, real estate, mapping, and emergency response because of their ability to capture real-time data from previously inaccessible angles.
Types of Drones
Drones come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications. Understanding these types can greatly aid in selecting the right drone for your needs, whether for personal use or professional applications. Here’s a breakdown of some popular types:
- Quadcopters:
- Description: The most common type of consumer drone, with four rotors.
- Uses: Photography, videography, recreational flying, and racing.
- Example: DJI Phantom series.
- Fixed-Wing Drones:
- Description: Resemble traditional airplanes, featuring wings for lift and longer flight times.
- Uses: Surveying, mapping, and agriculture.
- Example: senseFly eBee X.
- Multi-Rotor Drones:
- Description: Includes drones with three or more rotors, which offer stability.
- Uses: Lifting heavier payloads, inspections, and aerial maneuvers.
- Example: Yuneec Typhoon series.
- Hybrid Drones:
- Description: Combines features of both fixed-wing and multi-rotor drones, offering flexibility.
- Uses: Long-distance travel and vertical takeoff capabilities.
- Example: Pipistrel Alpha Electro.
- Racing Drones:
- Description: Built for speed and agility, often customized by hobbyists.
- Uses: Competitive drone racing.
- Example: Fat Shark 101.
- Delivery Drones:
- Description: Designed specifically for transporting goods and packages.
- Uses: Logistics and supply chain.
- Example: Amazon Prime Air drones.
- Industrial Drones:
- Description: Equipped with advanced sensors for specific tasks, used in inspection and agriculture.
- Uses: Inspecting power lines, agricultural monitoring, and emergency response.
- Example: senseFly eBee X Ag.
Each drone type serves its unique purpose, and the choice largely depends on your objectives. For instance, if you crave thrilling experiences, racing drones would significantly feed that adrenaline rush, while delivery drones are at the forefront of logistical transformation. While these historical milestones and drone categories lay the foundation, it’s essential to recognize the growing importance of drone identification as they become integrated into our lives. Whether for regulatory reasons, safety precautions, or security enhancements, understanding how these machines operate will only enrich your knowledge as a drone enthusiast or professional. In conclusion, the rich history of drones paints a picture of innovation driven by necessity, and the types of drones available today cater to various needs across industries. From military applications to personal enjoyment, drones have certainly carved their niche in the modern world. As you explore further into the realm of drones, consider the impact of drone identification and security in shaping the future. Stay tuned to discover more on these vital topics!

Importance of Drone Identification
As drones continue to pepper our skies, the importance of drone identification has become increasingly paramount. Not only do these regulations and security measures serve to protect airspace and individuals, but they also advocate for responsible drone usage. Let’s delve into why identifying drones is crucial and explore the regulations and security concerns surrounding this topic.
Regulations on Drone Identification
Drone regulations are evolving rapidly as governments around the world recognize the potential risks associated with UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles). The primary aim of these regulations is not just about controlling air traffic but promoting safe and responsible flying practices.
- Remote Identification Rule: The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States, for example, has implemented a Remote ID rule, akin to a digital license plate for drones. This rule requires most drones to broadcast their ID and location data, which can be received by other aircraft and ground stations. Here’s why it matters:
- It enhances situational awareness among aviators.
- It assists law enforcement agencies in tracking and addressing unauthorized or unsafe drone operations.
- Registration Requirements: Many countries have established protocols surrounding the registration of drones. For instance, in the U.S., all drones weighing over 0.55 pounds (250 grams) must be registered. This promotes accountability among drone users.
- Registration often involves providing personal information, which helps streamline investigations if a drone is suspected of committing a violation or a crime.
- Local Regulations: Beyond national guidelines, local authorities may have additional regulations according to the specific needs of municipalities. For instance, cities may prohibit drone flights over crowded areas, parks, or certain sensitive buildings.
- Certification and Training: A critical aspect of responsible drone usage is ensuring that pilots are trained and certified. While recreational users might not require extensive training, commercial drone pilots must often pass examinations and adhere to rigorous operational guidelines.
Understanding these regulations helps you navigate the skies responsibly, knowing you’re contributing to a safer aerial environment.
Security Concerns in Drone Usage
While drones spotlight innovative capabilities, they also present considerable security concerns, primarily pertaining to privacy, safety, and potential malicious uses.
- Privacy Violations: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras can inadvertently infringe on privacy rights. Imagine a hobbyist drone operator flying their quadcopter to capture breathtaking scenery but unintentionally recording private moments of individuals unaware of the intrusion.
- Preventive Measures: Protecting public privacy can involve regulations that limit camera usage in certain areas, similar to the rules governing CCTV usage.
- Airspace Incursions: Unauthorized drone flights can lead to significant danger, particularly around airports. Instances where drones have disrupted flight paths have raised alarms. In one notable case, flights were suspended at London Gatwick, leading to massive delays due to unauthorized drone activity.
- Safety Regulations: This danger underscores the need for comprehensive regulations that prevent such incursions, including mandatory licensing, training, and strict enforcement of designated flight areas.
- Malicious Intent: Drones have the potential to be used for nefarious purposes—think of smuggling contraband, conducting surveillance, or even carrying out attacks. Notably, in 2018, an assassination attempt on a Venezuelan president involved a drone.
- Security Protocols: To combat such threats, countries are developing counter-drone technologies, including jammers and specialized detection systems to monitor airspace for rogue UAVs.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Drones rely on remote control systems, which can potentially be hacked or jammed. Imagine a drone that becomes unresponsive, uncontrollably flying into crowded areas—or worse, into restricted airspace.
- Securing Communication Channels: Implementing strong encryption measures can safeguard not only communication channels but also the data drones collect, ensuring integrity and security.
As drone technology grows, security issues will likely evolve. Understanding these risks is vital for all drone operators, whether recreational or commercial, as responsible use builds trust and supports innovations in drone applications. In conclusion, drone identification carries significant importance in ensuring accountability, safety, and respect for privacy. As regulations become more robust and security measures are enhanced, drone enthusiasts and operators alike must stay informed and vigilant. Making informed decisions strengthens the entire community’s commitment to a responsible and enjoyable drone-flying experience. So, as you prepare for your next flight, remember that awareness and compliance can significantly impact the future of drone technology. Let’s keep our skies safe and sound!

Current Methods of Drone Identification
As we venture deeper into the world of drone technology, we encounter an exciting array of methods designed to facilitate drone identification. Two leading techniques underpinning this effort are Remote Identification Technology and Geofencing Systems. Understanding how these methods work can give you a clearer idea of how to operate drones safely and responsibly.
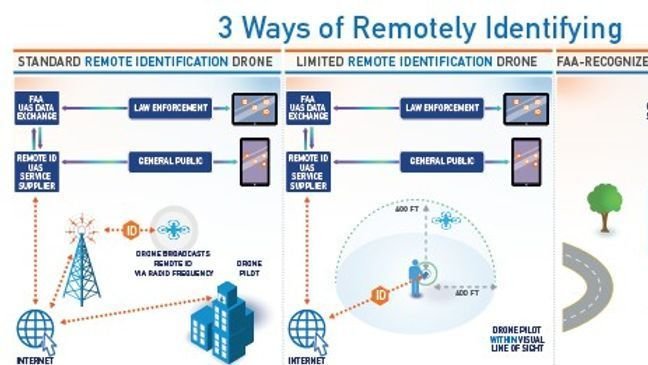
Remote Identification Technology
Remote Identification Technology has revolutionized drone operations by enabling real-time tracking and identification of drones flying in shared airspace. Imagine a world where each drone has a digital footprint, making it easier to monitor its activities. This technology operates much like a digital license plate for drones, seamlessly broadcasting critical information that enhances airspace safety and accountability.
- How It Works: Remote ID technology involves the transmission of data through various protocols, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. The available information typically includes:
- Drone ID: A unique identifier that associates the drone with its owner.
- Location Data: GPS coordinates allowing for precise tracking of the drone’s position.
- Altitude: The drone’s elevation to ascertain how high it’s operating.
- Velocity: Information on the drone’s speed.
- FAA Regulations: In the U.S., the FAA has mandated that most drones must implement Remote ID technology. As of September 2023, all drones above a particular weight must either broadcast their Remote ID information or have the capability for it. This regulation fosters an environment of transparency and safety.
- Benefits of Remote Identification:
- Increased Safety: With real-time tracking, air traffic controllers and law enforcement can monitor drone activity, reducing incidents of airspace violations.
- Enhanced Accountability: Owners can be held responsible for their drones’ actions; this creates a sense of ownership and fidelity within the drone community.
- Support for Law Enforcement: If a drone is used inappropriately or unregistered, authorities can quickly identify the owner and take necessary action.
- Example in Action: Consider a scenario at a public event, like a music festival. With hundreds of drones potentially flying overhead, Remote ID can help authorities differentiate between authorized photography drones and potential intruders, maintaining safety and privacy simultaneously.
While Remote ID technology offers a promising solution to many challenges, it’s essential that all drone enthusiasts are familiar with its operations. As we look forward, let’s explore another critical method in drone identification: geofencing systems.
Geofencing Systems
Geofencing is a technology designed to create virtual barriers that outline specific geographic boundaries for drone operations. This method is crucial for ensuring that drones operate safely while preventing unauthorized flights in sensitive areas.
- How Geofencing Works: By utilizing GPS or RFID technologies, geofencing allows operators to set defined boundaries for drone activities. Drones equipped with geofencing systems will automatically receive alerts or restrict their flight if they attempt to enter or exit the designated area.
- Types of Geofences:
- Soft Geofences: These merely inform the drone pilot of the restriction. The pilot can choose to override the warning. Think of it as a gentle reminder—“Hey! You’re about to enter restricted airspace.”
- Hard Geofences: These actively prevent the drone from crossing into restricted areas. Imagine trying to enter a no-fly zone near an airport, only to discover your drone won’t budge. This is the power of hard geofencing.
- Implementation of Geofencing: Many modern drones come pre-loaded with geofencing capabilities. For instance, DJI drones have built-in databases that recognize airport locations and other restricted zones. This means your flying experience is safeguarded against entering high-risk areas.
- Benefits of Geofencing Systems:
- Safety Assurance: By restricting flights in sensitive areas, geofencing supports the safety of both drone pilots and those on the ground.
- Encouragement of Responsible Flying: Geofencing promotes responsible flying and cultivates better habits by encouraging operators to remain aware of their surroundings and legal obligations.
- Emergency Response: In natural disasters, authorities can use geofencing to delineate safe zones for drone operations, ensuring drones can assist with surveillance and assessment without impeding emergency services.
- Real-world Application: Imagine you’re out for a leisurely day of flying your drone over a stunning landscape. Suddenly, your drone signals you’re approaching a geofenced area near a military base. You’re alerted and can safely redirect your drone, preventing a potentially serious violation of regulations. How cool is that?
In a nutshell, Remote Identification Technology and Geofencing Systems serve as critical pillars of the modern drone ecosystem, enhancing safety and accountability in our shared skies. Both methods play a vital role in promoting responsible drone usage and are essential tools for operators to master. By familiarizing yourself with these technologies, you contribute to safer airspace and a more effective and vigilant drone community. As drone technology continues to advance, the mechanisms for identification and regulation will only grow in importance. Stay informed, remain compliant, and enjoy every flying experience, as the skies are yours to explore—safely!

Challenges in Drone Identification
As the world of drones continues to expand, so too do the complexities surrounding drone identification. While technological advancements have made significant strides in enhancing safety and accountability, certain challenges still loom large. Two major hurdles in this realm are counterfeiting and cloning, as well as the difficulties associated with tracking unidentified drones. Let’s unpack these issues more deeply to understand their implications and potential solutions.
Counterfeiting and Cloning
With the increasing popularity of drones, the counterfeiting and cloning of drone components and identification systems have emerged as pressing concerns. Just like any high-demand technology, drones have become a target for dishonest practices, posing risks not only to individual operators but also to public safety at large.
- Understanding the Issue: Counterfeiting refers to the production of fake parts or drones that mimic legitimate products, while cloning involves replicating unique identifiers and functionalities from one device to another.
- Example: Imagine purchasing what you thought was an authorized battery for your drone, only to find that it’s a counterfeit. Such false products can malfunction, leading to crashes and loss of access.
- Risks of Counterfeiting:
- Safety Concerns: If a counterfeit product fails mid-air, it can lead to crashes, potential injury, and damage to property.
- Legal Ramifications: When an unregistered or cloned drone is involved in illegal activities, it can lead authorities back to innocent operators mistakenly associated with these actions.
- Cloning in the Drone World: Cloning doesn’t just stop at hardware—malicious actors can replicate remote identification signals, leading to a lack of accountability.
- Impact: Drones that have their unique identifiers cloned can be used anonymously to commit crimes, such as smuggling or surveillance.
To combat these issues, manufacturers and regulatory bodies are ramping up efforts to implement anti-counterfeiting technologies and secure registration systems. Potential measures include:
- Watermarking and Serialization: Incorporating unique marks on drone parts to assure authenticity.
- Blockchain Technology: Using blockchain to create a tamper-proof registry of drones and their components, ensuring traceability.
While these are steps in the right direction, continued vigilance from both manufacturers and drone operators is vital to ensure safety and integrity in the field.
Issues with Tracking Unidentified Drones
Tracking unidentified drones is becoming an increasingly complex challenge as the number of drones in the sky continues to rise. The absence of identification has raised alarms in terms of security, safety, and privacy.
- The Challenge of Unidentified Drones: Think about the last time you attended an outdoor festival or a crowded event. Drones buzzing overhead could create a chaotic situation if their origins remain unknown—and that’s precisely the concern with unidentified drones.
- Unidentified drones can threaten public safety by intruding on restricted airspace or interfering with manned aircraft operations.
- The Limitations of Current Systems:
- Inconsistent Compliance: Not all drone operators adhere to regulations like Remote ID rules. Hobbyists and recreational users, in particular, might fly drones without the necessary identification systems in place.
- Urban Environments: The proliferation of high-rise buildings and dense structures makes it challenging to track drones, as signals can become obstructed or distorted.
- The Security Risks: Unidentified drones can be leveraged for malicious purposes, including spying or even attacks. Cases have emerged of drones being utilized to carry out sabotage or to gather intelligence without oversight.
- Example: In 2020, several incidents of unidentified drones flying over sensitive areas, such as industrial plants and military bases, prompted national security agencies to raise flags.
Addressing the problem of unidentified drones calls for new strategies and technologies, such as:
- Enhanced Detection Technologies: Tools like radar systems specifically designed for drone detection can help identify and track unmanned aircraft in real-time.
- Community Reporting: Encouraging members of the community to report suspicious drone activity can aid law enforcement in quickly responding to incidents. A local example could be neighborhood watch programs that train citizens to recognize compliant drone behaviors versus illicit ones.
- Collaboration with Third Parties: Involving technology companies in advancing detection systems could lead to innovative solutions that enhance tracking capabilities, akin to how other tech sectors have collaborated on safety issues.
- Public Awareness and Education: Teaching drone pilots about the importance of identification, adherence to local regulations, and the potential risks of flying unidentified can foster a culture of responsibility and safety.
In conclusion, while significant advancements have been made in drone identification, various challenges—like counterfeiting and issues with tracking unidentified drones—persist. Engaging in measures to refine technologies, enhance community awareness, and implement stringent regulations will be crucial for navigating these challenges. As a drone enthusiast, staying informed about these issues can make a significant difference in not only fostering a safer flying environment for yourself but for everyone in your community. The sky is full of possibilities, and ensuring safety and accountability will help us enjoy these advancements while minimizing risks. Let’s keep pushing for responsible practices, and together, we can soar to new heights!

Future Trends in Drone Identification
As we navigate through the evolving landscape of drone technology, the future of drone identification holds exciting possibilities. With the ongoing challenges facing the industry, innovative solutions like blockchain technology for drone registry and artificial intelligence for monitoring are emerging as powerful tools. Let’s explore these trends in-depth and see how they can shape the future of drone operations for both enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Blockchain Technology for Drone Registry
Blockchain technology, which gained fame as the backbone of cryptocurrencies, is making waves across various industries, including drone identification. At its core, blockchain offers a decentralized and tamper-proof method for recording and verifying information. So, how exactly can this technology revolutionize drone registration and identification?
- Immutable Records: Imagine a world where every drone has an immutable record of ownership, flight history, and compliance with regulations. Blockchain can provide each drone with a unique digital identity stored on a distributed ledger, making alterations nearly impossible.
- This feature not only promotes accountability among drone owners but also helps in tracking the origins of drones used in illicit activities.
- Decentralization: By leveraging decentralized networks, the responsibility of registration and verifiable data sharing shifts from a central authority to a community-driven process. This could potentially streamline registration procedures, enabling more efficient tracking of drone activity without excessive bureaucracy.
- Seamless Transactions: Blockchain can simplify the transfer of drone ownership through smart contracts, reducing barriers for sellers and buyers and ensuring all transactions are securely documented.
- Think of a future where you can effortlessly buy and sell drones while ensuring that all ownership history and regulatory compliance is transparently available.
- Case Study: A few companies are already spearheading pilot projects using blockchain for drone registrations. For instance, a U.S.-based startup is developing a system for secure drone tracking, allowing for real-time identification and visibility across various stakeholders, including law enforcement and regulatory agencies.
Benefits of Implementing Blockchain in Drone Registration:
- Enhanced Security: Higher security measures ensure that all data regarding drone registration, ownership, and compliance is safe from tampering.
- Increased Transparency: Access to a publicly verifiable registry fosters trust among drone operators, regulators, and the public.
- Reduction in Fraud: As the system becomes more robust, reduced risk of counterfeiting and cloning arises, further solidifying the integrity of drone operations.
As you can see, blockchain technology holds significant potential for transforming drone identification and registration, making the skies safer and more responsible for everyone involved.
Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Drone Monitoring
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is another game-changer for drone identification, providing sophisticated solutions to monitor, analyze, and manage drone operations in real-time. With AI-driven technology, we can expect advancements that enhance situational awareness and enable more effective governance of aerial space.
- Real-time Monitoring: AI can process vast amounts of data quickly, enabling real-time monitoring of drone activities. Imagine an operational environment where law enforcement can leverage AI systems to identify drones that exceed altitude limits or enter restricted airspace instantly.
- Example: An AI surveillance system might integrate with drone Remote Identification Technology, cross-referencing flight paths and performing automatic notifications when unregistered drones enter sensitive airspace.
- Predictive Analytics: By gathering historical flight data, AI can discern patterns and predict potential malfunctions or security threats related to drone operations. This predictive analysis could extend to various scenarios, such as unauthorized flights or flights in dangerous weather conditions.
- This means drone operators can receive alerts about incoming storms or other risks, allowing for timely interventions.
- Drive Autonomous Compliance: As drones become more advanced, AI can play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Imagine drones equipped with AI that adheres to local regulations autonomously, keeping pilots informed only when intervention is required.
- Regardless of whether you’re operating a commercial drone for deliveries or capturing aerial shots for a project, these AI features can operate as an invaluable partner.
- Use of Computer Vision: AI systems leveraging computer vision can analyze footage from drone cameras in real-time and alert operators about potential safety hazards. If a drone inadvertently approaches a no-fly zone or enters restricted airspace, the AI can swiftly notify operators or even initiate a safe landing procedure.
Benefits of AI Integration in Drone Monitoring:
- Efficiency: Automation of monitoring tasks not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of human error.
- Increased Safety: Real-time threat detection enhances overall safety, particularly in crowded urban environments or high-traffic areas.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AI-driven solutions can lower operational costs by improving flight management and reducing incidents of safety violations.
Looking ahead, the combination of blockchain technology for drone registry and AI solutions for monitoring creates a powerful synergy that promises to enhance the safety, accountability, and efficiency of drone operations. In conclusion, the future of drone identification is brimming with innovative solutions that leverage the power of the latest technologies. Staying informed and adopting these advancements is essential for enthusiasts, operators, and regulators alike. Your engagement with these emerging technologies not only fosters a safer flying environment but helps shape the future of aerial exploration. So, whether you’re a drone pilot or an interested observer, be prepared to embrace the incredible innovations on the horizon! The sky is indeed the limit! 🚀